In my search for a comprehensive guide for optimizing Bluetooth Low Energy power consumption, I found multiple guides from different vendors. These guides were great, but were more focused on specific chips and modules from the vendors.
My goal here is to summarize the findings and make this a comprehensive guide for anyone looking to optimize Bluetooth Low Energy power consumption and achieve maximum battery life – no matter which vendor you end up choosing. More specifically, I'll be focusing on optimization for BLE peripheral devices and not BLE central devices.
By the end of this article, we'll have answered these key questions:
Why is reducing power consumption important for BLE devices?
What is the average power consumption of BLE modules?
What are the main ways to achieve low power consumption?
Which BLE parameters should be tuned?
What should be measured when optimizing power consumption?
How to measure power consumption?
Why Optimize Power Consumption for BLE Devices?
Many new electronic products – whether consumer, medical, industrial…etc – are moving towards being powered by batteries. Some of the reasons behind this:
- Modules and chips are becoming more power efficient, so more applications and use-cases can be run on battery-powered devices without requiring the end user to change the battery too often (think 6+ months).
- The explosion of the Internet of Things applications and devices, where data is being captured for all types of environments and scenarios, requiring more flexibility and use of completely wireless solutions.
- Chips and modules are becoming much smaller physically, allowing you to embed them within small devices.
As a result of these trends, the need for optimizing power consumption to extend battery life in BLE devices has become increasingly crucial, especially for certain applications including:
- Remote health monitoring: Wearable medical devices such as heart rate monitors, glucose meters, and blood pressure monitors require long battery life to ensure continuous and reliable monitoring of patients' health.
- Asset tracking: BLE beacons and trackers used for monitoring the location of valuable assets in various industries (logistics, manufacturing, agriculture) need to function for extended periods without frequent battery changes, as constant maintenance can be time-consuming and expensive.
- Environmental monitoring: IoT sensors that measure air quality, temperature, humidity, or water levels in remote areas need to operate efficiently for long periods since it's often difficult and costly to perform routine battery replacements.
- Smart agriculture: BLE-enabled devices that help farmers monitor soil moisture, nutrient levels, and crop health must have a long battery life to ensure consistent and accurate data collection.
By focusing on power optimization, developers can create devices that deliver exceptional performance and reliability, ultimately enhancing user experience and meeting strict battery life requirements.
What is the average power consumption of a BLE module?
BLE modules are generally designed to be low power, but the current draw between modules can vary greatly based on the specifics of the device design, chip selection, and software implementation.
Generally, you can expect the following, based on the state the device is in:
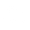
In the idle state, the BLE device isn't doing anything, so it's mostly in low power or sleep mode. The current draw can be very low, often in the microamp (µA) range, sometimes even less. For example, it might be somewhere around 1 µA to 10 µA, depending on the specific chip and power-saving features used.Here you can see the current consumption during deep sleep mode:
Current consumption during deep sleep mode (Source: "Silicon Labs - Optimizing Current Consumption in Bluetooth Low Energy Devices")
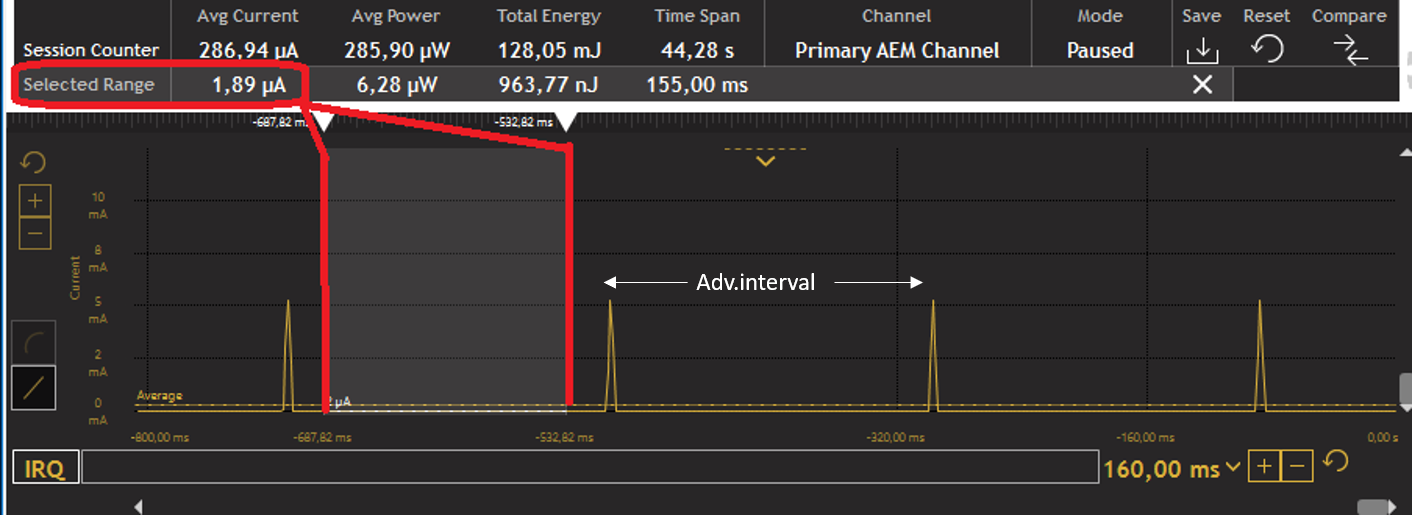
During advertising, the device's radio is on and actively broadcasting packets to let other devices know it's there. This takes more power, but it's usually done in short bursts. Current draw during these bursts might be in the range of 3 milliamps (mA) to 10 mA, again depending on the specifics of the device and the advertising settings (like advertising power level, interval, and payload size). For example, you can see an iBeacon's average current consumption at various advertising intervals here:
iBeacon average current consumption at various advertising intervals (Source: "Silicon Labs - Optimizing Current Consumption in Bluetooth Low Energy Devices")
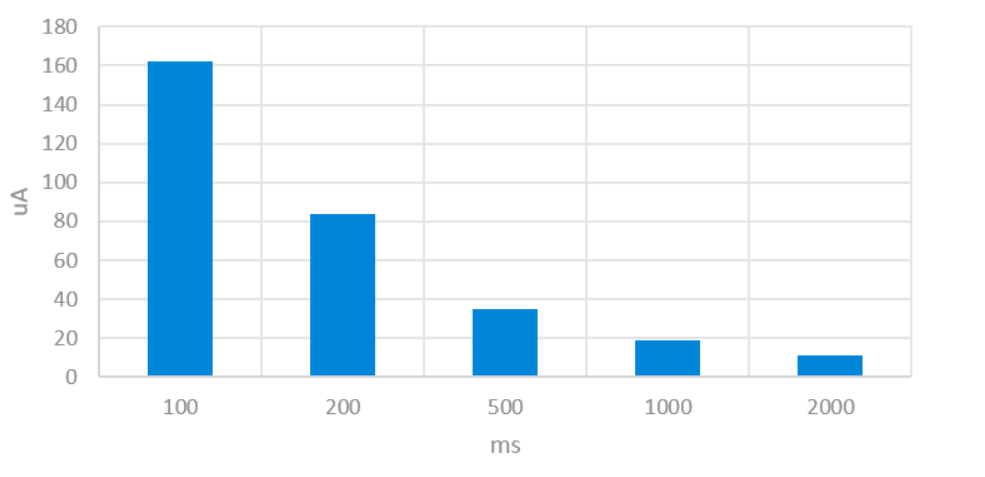
- During connection, the device is actively communicating with another BLE device. The power usage can vary significantly based on the Bluetooth connection settings, like connection interval and connection event length.
However, it might be in a similar range to the advertising state, perhaps around 5 mA to 30 mA (give or take a few mA) during active communication. But keep in mind that this is often averaged out over time since the device is typically not constantly transmitting or receiving data. Between data transmissions, the device can go into a lower power mode, as you can see demonstrated here:
Current consumption during a 15 ms connection interval (Source: "Silicon Labs - Optimizing Current Consumption in Bluetooth Low Energy Devices")
These are only rough estimates, and the actual current draw can vary a lot based on the specifics of the device design and usage.
The 3 main ways to minimize power consumption
At a high level, energy consumption is mainly decreased in microcontroller applications, and embedded systems in general, by reducing radio communication and increasing sleep/idle cycles as much as possible.
In theory, this sounds simple and straightforward. However, when trying to accomplish this in practice, it can be much more complicated. For example, variables such as the changes in the environment (temperature, humidity, obstacles, and radio interference causing transfer retries) make the task exponentially more difficult.
There are three ways to minimize power consumption:
- Choose the right hardware components – including the battery.
- Optimize the firmware via static configurations (such as peripheral bus speeds and pin configurations) and dynamic/run-time parameters (such as Bluetooth low energy parameters).
- Optimize firmware source code in terms of both: writing efficient code and using the right compiler optimizations (for speed and size) can help you achieve your low power goals. This also includes your system design for protocol efficiency and packet sizes being transferred over the air or to/from external peripherals.
In this post, I’m focusing on Bluetooth Low Energy devices (rather than Bluetooth Classic (BR/EDR) devices) and how to optimize the different Bluetooth Low Energy parameters.
Again, it all basically comes down to how long your MCU spends in idle/sleep mode vs. active mode. User experience is the most important in determining the changes and parameters that could potentially affect power consumption. Make sure it’s always the top priority for your product.
💡 Looking for more BLE tutorials? Enroll in the Bluetooth Developer Academy today and get exclusive access to 300+ hours of course content built exclusively for developers, by developers.
Which BLE parameters should be tuned?
Optimization is achieved by tuning the parameters for the two states of Bluetooth LE devices:
Connected state
Connection interval (connInterval):
Ranges from 7.5 milliseconds to 4 seconds (in multiples of 1.25 milliseconds).
Peripheral latency (connPeripheralLatency):
Allows a peripheral to skip connection events without the central device dropping the connection. Thus, a peripheral device can skip several connection events, especially if it does not have additional data, resulting in power savings.
The Peripheral Latency ranges from 0 to ((connSupervisionTimeout/ connInterval) – 1).
A peripheral latency of 0 means the peripheral is not allowed to skip any connection events.
Connection supervision timeout (connSupervisionTimeout):
Defines the maximum time between two received Data Packet PDUs before the connection is considered lost. The connSupervisionTimeout shall be a multiple of 10 ms in the range of 100 milliseconds to 32.0 seconds, and it shall be larger than (1 + connSlaveLatency) * connInterval.
Advertising state
Advertising interval:
Theoretically, it ranges from 20 milliseconds to 10,485.759375 seconds (yes, you read that max number right!). However, most stacks cap the maximum to a smaller number, usually 10.24 seconds. The longer the interval, the less current the device will consume during the advertising state. This is a more important parameter when working with broadcast-only devices such as beacons.
For connected devices, increasing the advertising interval will have a limited impact on energy savings after a certain point: the current consumption will be lower during the advertising state, however, the central will take longer to find the advertising device causing the advertising period to be higher (which may lead to higher power consumption than in the case where the advertising interval is shorter).
For some scenarios, it may be beneficial to advertise periodically instead of advertising all the time. The advertising period can then be tuned to achieve the optimal user experience.
For example, it is also a best practice to advertise at a lower interval (higher frequency) in the beginning (say for 30 seconds or so) and then switch to a longer advertising interval. This can be upon boot-up or based on some user interaction (like pressing a button) and allows the central device to discover the peripheral much faster if it's in range while also allowing the peripheral to reduce power if not discovered or connected to by a central after that initial period.
Advertising data length:
Another parameter affecting current advertising consumption is how many payload bytes are sent in each advertising packet. Therefore, it may be beneficial in terms of current consumption to only place primary advertising data in the advertising packet and place all secondary data in the scan response packet, as advertising packets are sent much more frequently than scan response packets.
If you plan to transfer data in large bursts you may exceed the recommended peak, which may negatively impact both the capacity and lifetime of the battery. For sending large quantities of data, look for ways to optimize the transfer:
- Adjust connection intervals, advertising intervals, and peripheral latency parameters accordingly.
- Combine small packets into fewer large ones (enable Data Length Extension (DLE), introduced in version 4.2 of the core specification).
- Compress data before transmission.
- Send lower priority data at slower rates.
- For sensor-based devices, only measure and prepare data if the client has subscribed to the associated characteristic. The same is true on the other side (on the client/mobile side), only subscribe to characteristics that you’re interested in.
- Consider how much of the time the device will be used. If the device will mostly stay in the idle state, then focus on optimizing the power consumed during the sleep state as much as possible. Conversely, if the device will be active most of the time, then focus on reducing the active-state current draw.
One last thing to keep in mind is to test with debug mode turned off since BLE power consumption will usually be higher than with debug turned off.
What to measure?
It is not possible to compare the power consumption of a BLE device to another using a single metric. Sometimes a device gets rated by its “peak current”. While the peak current plays a part in the total power consumption, a device running the BLE stack will only be consuming current at the peak level while it is transmitting.
Even in very high throughput systems, a BLE device is transmitting only for a small percentage of the total time that the device is connected. In a typical application, a device running the BLE stack will spend most of the time in a sleep state between connection events. The primary metric that takes these other time and current measurements into account is the “average current”. It is this value that can be used to determine the battery life of a BLE device.
Note that a single “average current” value cannot be given for a device in its datasheet or in the device’s specifications, as the average current is highly dependent on the connection parameters used. Anytime an “average current” specification is given, it is very important to understand the exact use case in which the measurement was made.
With that said, here are some other useful metrics that should be kept in mind:
- Peak current: useful when comparing to what the battery vendor indicates as the recommended maximum peak – going above the value may negatively impact the capacity and lifetime of the battery.
- How much power is used to transfer a certain amount of data
- Sleep-state current consumption
How to measure Bluetooth power consumption?
Now, let’s talk about testing the power consumption of your device. The most important thing is to ensure you test in an environment as close as possible to what a user’s environment would be like (real-life testing and not just in a lab setting). This will make your estimations much closer to real-life usage and ultimately make your users much happier.
- The simplest way to measure current with an oscilloscope is to use a current probe and directly monitor the current going into the system.
- If you do not have a current probe available, an easy alternative is to use a small resistor in line with the power supply input to the system. You can then use a standard oscilloscope voltage probe to measure the voltage across the resistor and effectively measure the current by dividing the voltage by the resistance. A good resistor value to use is 10 Ω, as this value is small enough that it shouldn’t affect the existing circuitry and large enough to provide a voltage that can be measured with decent precision (in addition, using a value of 10 Ω makes the calculations very simple).
- When performing measurements, it is best to use a regulated DC power supply as opposed to an actual battery. This eliminates variables that might be caused by a defective or low battery.
- Other methods of measurement include specialized hardware and software solutions provided by the vendor of the chip/module you’re using. For example, Silicon Labs provides the Energy Profiler tool as part of Simplicity Studio. Nordic Semiconductor provides the Nordic Power Profiler Kit (PPK).
Summary and Closing
Ultimately, each application will dictate how low your device’s power consumption can get. If the parameters are modified to a point where they negatively affect the user experience, then this will not help your product or users. Always keep the user experience (UX) as the top priority and design the system (including power optimization) in a way to enhance the UX.
Finally, I will leave you with a summarized list of points/questions to keep in mind when optimizing your BLE device’s power consumption:
- How long will it run on a coin cell battery?
- What’s the current draw at peak usage?
- How much power is used to transfer a certain amount of data?
- How much data does the app need to transfer?
- How often does it need to transfer data?
- The battery capacity declared by the manufacturer is in ideal conditions.
- Keep in mind that longer periods of peak current draw can affect/damage the battery.
- If the power source is current-limited, then the peak current is just as important as the average current.
- If you plan to transfer data in large bursts, you may exceed the recommended peak current, which negatively impacts both the capacity and lifetime of the battery.