Sponsored by Silicon Labs
Introduction
Over the years, Bluetooth Low Energy has proven to be great for establishing a connection between two devices and maintaining it within a reasonable RF range. As we already know, connections are the way to go for applications that require consistent bidirectional data communication between two Bluetooth LE devices.
However, connections rely on the two Bluetooth LE devices being within a reasonable RF range of each other in order to be maintained. But what if you have an application where a Bluetooth LE medical device must constantly be connected within a large area (e.g., a medical facility) to relay its sensor readings to a cloud server? In such a scenario, deploying a single Bluetooth LE gateway may not be sufficient (especially for large coverage areas).
The natural solution here is to deploy multiple Bluetooth LE gateways to maintain a more comprehensive connection to the Bluetooth LE sensor.
But how do you manage the connection from multiple gateways to a single device? And how do you make it seamless across these gateways?
Let’s imagine another scenario where you have a Bluetooth LE-enabled mobile device connected to a Bluetooth LE-enabled vehicle access control system. In this case, RSSI measurement from the vehicle could be utilized to approximate the distance of the mobile device. However, RSSI is prone to many environmental factors, and its accuracy is usually unsatisfactory.
One solution to this is to add multiple Bluetooth LE devices within the vehicle to monitor the RSSI of the mobile device and employ trilateration to determine better location accuracy.
But again, how do you manage this without overcomplicating the implementation? And how do you ensure that the multiple nodes are able to consistently monitor the RSSI?
To address these traditional problems with Bluetooth LE (limited RF range and inaccuracies of RSSI), Silicon Labs just introduced a new feature in their Bluetooth SDK called the Bluetooth Connection Analyzer.
This new feature is available in Silicon Labs' Bluetooth SDK version 7.0.1.0.
The Bluetooth Connection Analyzer
So, what is the Bluetooth Connection Analyzer? Simply put, it’s a simplistic Bluetooth sniffer implementation that allows multiple devices to measure the RSSI levels on 3rd party devices connected to a friend device by monitoring the connection between this device and the 3rd party devices.
You are probably asking, well, what makes this feature special? And how does it make my life easier?
Great questions!
With this new feature, with just a few API calls, you can enable friend nodes to monitor the RSSI of a 3rd party device’s connection with a main device and utilize this information for multiple scenarios. Some of these include:
- Connection handover: where a device can roam within an area and remain connected to multiple Bluetooth LE gateway devices appearing as if they were one (trusted) device
- More accurate positioning: where a device’s location can be better estimated via multiple nodes measuring the RSSI of the connection between two trusted devices
Now, even though RSSI measurements of a device may be easily measured for non-connected devices (e.g., in advertising mode), it is much more difficult to achieve the same for connections, especially between bonded devices, which is where this new feature comes in!
How does it work?
Let’s run through the steps of how a system would utilize the Bluetooth Connection Analyzer feature by looking at the vehicle access control system example application we referred to earlier.
System Diagram
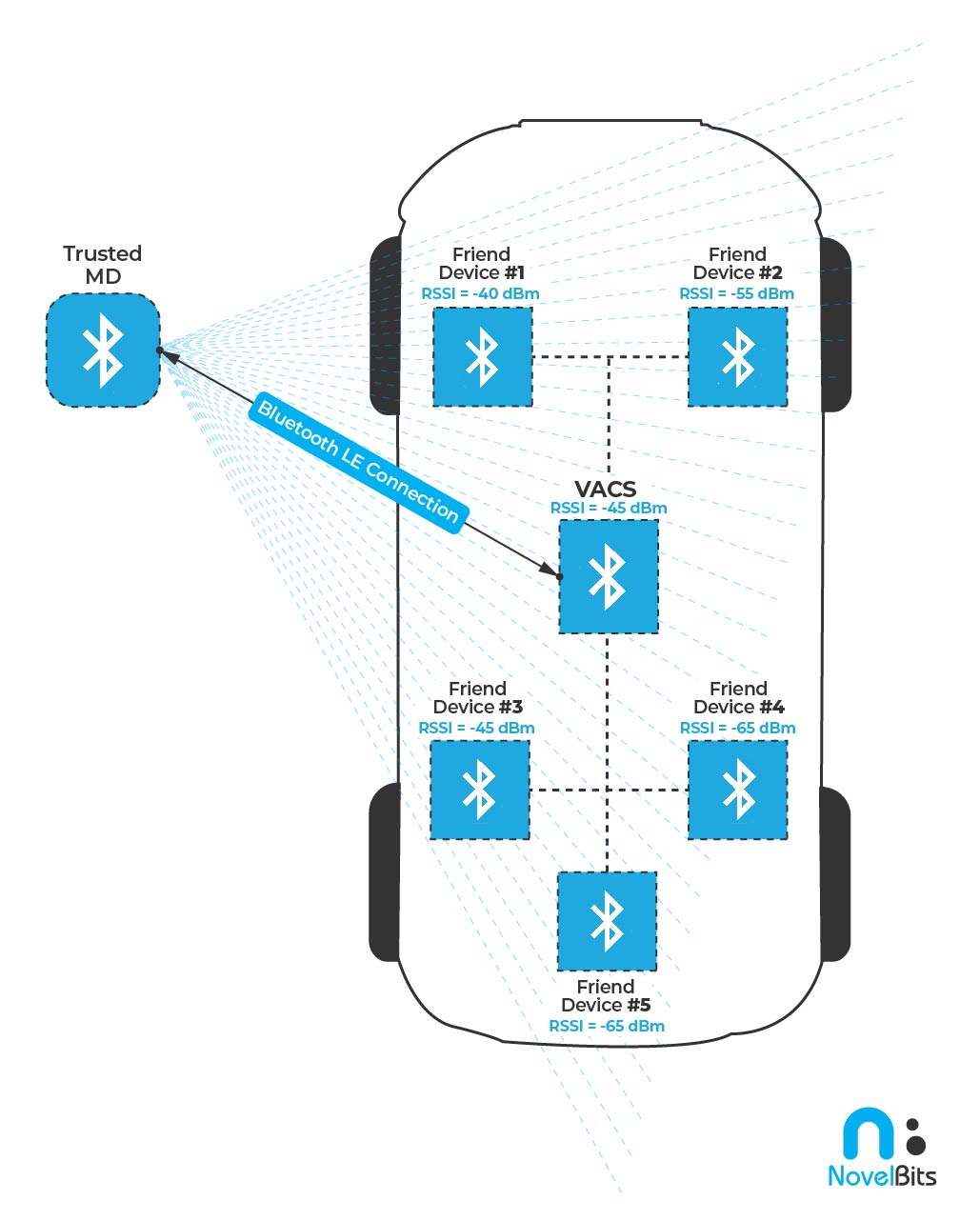
System Components
The system comprises the following main components:
- A Bluetooth LE-enabled Vehicle Access Control System (we'll refer to it as VACS)
- A Trusted Mobile Device that the user can utilize to unlock/lock the vehicle and perform other access control functions (we'll refer to it as Trusted MD)
- Multiple Bluetooth LE devices deployed within the vehicle at strategic locations. These act as trusted “Friend” Devices to the main access control system (we'll refer to them as Friend Devices – not to be confused with friend nodes in Bluetooth mesh!)
System Functionality
- VACS acts in the peripheral role and has a secure connection established with the Trusted MD
- A secure “connection” is established between VACS and the Friend Devices within the vehicle (this can be a wired or wireless communication channel)
- Once a connection is established between VACS and the Trusted MD, VACS can call an API (sl_bt_get_scheduling_details) to get all the details of the established connection (Access Address, CRC seed, channel map, channel selection algorithm, event counter, connection interval, bonding information, and more)
- VACS can then share this information with all the Friend Devices
- The Friend Devices can then pass this information to a new API called sl_bt_connection_analyzer_start() to start the Connection Analyzer and “follow” the connection for the purpose of monitoring the RSSI of the Trusted MD.
- Events from the stack are reported to each Friend Device with RSSI values for both the peripheral and central.
- These RSSI values for the Trusted MD are then shared back to VACS (via the wired or wireless channels), which can then utilize trilateration and other positioning algorithms and techniques to approximate the location of the Trusted MD in relation to the main system.
- Based on this calculated (approximate) position, the VACS can determine which operations are allowed or triggered automatically.
- For example:
- Determining whether the smartphone is within a certain radius of the vehicle, allowing the unlocking of the vehicle when a button is pressed on the Trusted MD (or automatically doing so)
- Determining whether the smartphone is inside the vehicle and allowing/disallowing certain actions.
- For example, if the smartphone is inside the vehicle, the vehicle can be turned on. It may also prevent auto-locking if the vehicle is in park mode and the user walks away, leaving the phone in the vehicle (preventing the user from locking themselves out).
How to Get Started with Connection Analyzer
Now that we've covered the basics of this new feature and gone through how it works in an example use case let's look at how you, as a developer or system architect, could utilize it and where to go from here.
Understanding the APIs Involved
The APIs you would use to utilize this feature are:
- sl_bt_connection_get_scheduling_details(): this API would be called from the primary device after it has established a connection to the third-party device. It would return all the information and details needed for the friend nodes to follow the connection between the primary and third-party devices.
- sl_bt_connection_analyzer_start(): this API would be called from the different friend nodes and supplied with the information retrieved from the previous API (sl_bt_connection_get_scheduling_details()) to start the process of monitoring the RSSI values for the third-party device.
- The stack will provide a report of the monitored RSSI values via a stack event of type sl_bt_evt_connection_analyzer_report_t, which contains central_rssi and peripheral_rssi. Depending on the role of the third-party device, the friend node would pass the corresponding RSSI values to the primary device.
- When multiple friend devices distributed in strategic locations within the field of interest are set up to provide this information to the primary device, it allows the primary device to formulate a much more accurate view of the location of the third-party device.
Sample Example using Connection Analyzer
Silicon Labs has published a great example application that utilizes Connection Analyzer. The Bluetooth Roaming example application is available on GitHub.
Sample Application Description:
This pair of examples models a medical application. The goal is to gather data from several Bluetooth LE heart rate (HR) sensors in a large facility using multiple access points (AP). Whenever a person with the HR sensor moves out from the radio range of an AP and loses connection, a nearby AP shall find it and continue the HR data collection. The access points are supervised by a network coordinator.
Source: Silicon Labs GitHub Repo – BT Roaming Example Application
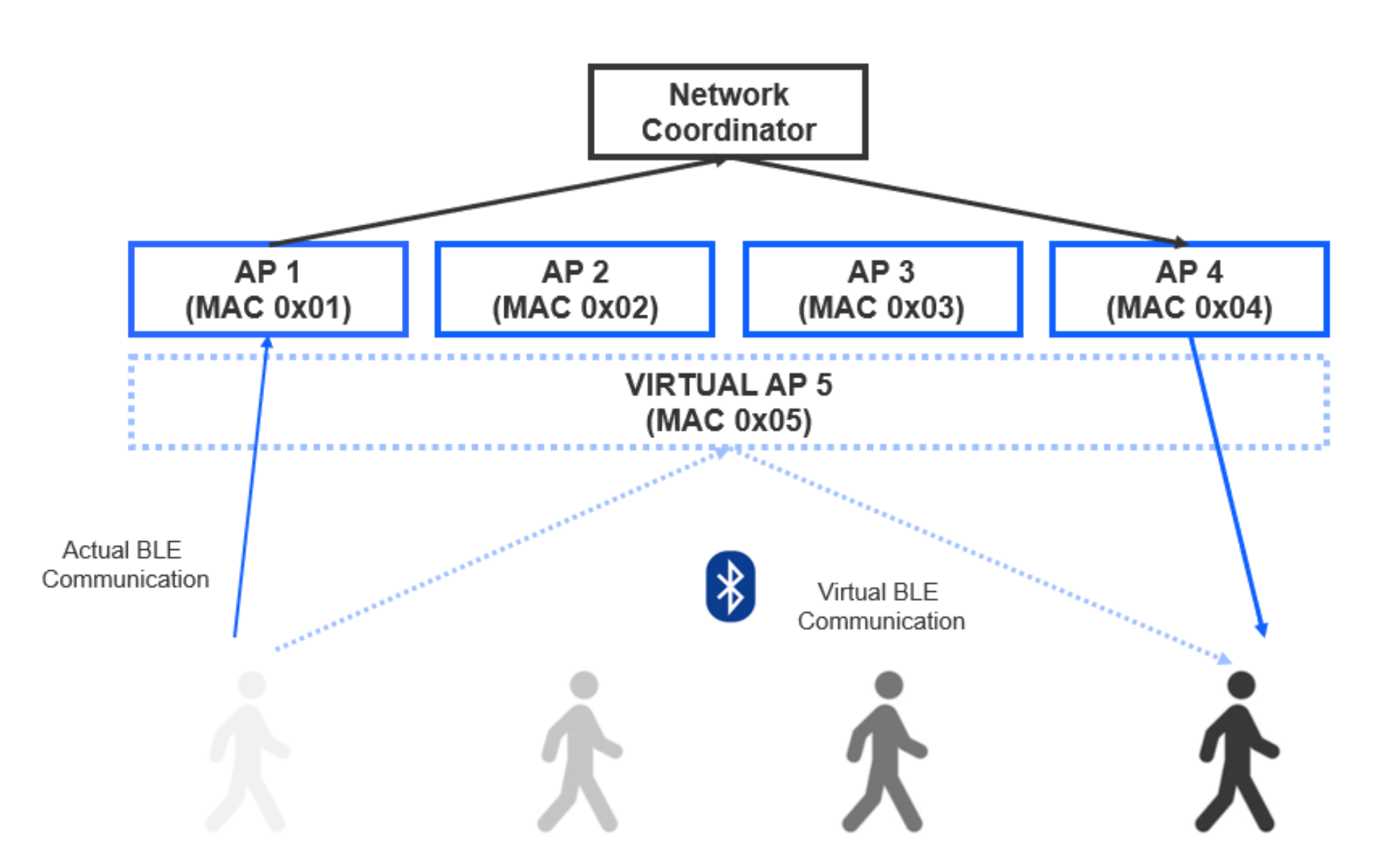
With this example, you can set up a system that maintains a Bluetooth LE connection to a moving medical device in order to continuously capture its sensor data. All this while making it a seamless connection handover from the medical device's perspective. The APs would appear to the medical device as a single device that ensures that the connection covers a large space (something that traditionally wouldn't be possible with a one-to-one Bluetooth LE topology).
Important Notes
Here are a few important things to keep in mind when implementing an application that uses the Connection Analyzer:
- The communication channel between the main and friend devices can be wired (UART, CAN bus, Ethernet) or wireless (Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, etc.). This is left up to the implementation as appropriate.
- As of now, only RSSI measurements are monitored by the Connection Analyzer (packet details are not captured)
- Friend devices can operate in NCP mode (controlled by an external host) or SoC mode.
- Changes in the connection parameters between the primary and third-party devices require resending the connection details to the friend devices.
- Bonding information can be shared from the primary device with the friend nodes to allow them to re-use this bonding relationship and make them appear to the third-party device as a single device that's also trusted.
Obviously, the APIs that provide this solution will still require some additional work on your part to fully utilize it. This would include designing the architecture of the system, such as the number of friend nodes, their distribution within the field of interest, their configuration (SoC or NCP mode), the communication channel used between the friend devices and the primary device (wireless or wired), how the data is shared between devices, etc.
Summary
In this post, we covered a new feature introduced by Silicon Labs to address a real problem with Bluetooth LE-based systems. The Connection Analyzer feature provides a solution for two main use cases:
- Connection handover: where a device can roam within an area and remain connected to multiple Bluetooth LE gateway devices appearing as if they were one (trusted) device
- More accurate positioning: where a device’s location can be better estimated via multiple nodes measuring the RSSI of the connection between two trusted devices