If you’re looking for a way to add BLE connectivity to your project, you have many options. So how do you know which module is right for you? We’ll help you understand the options available and make the best decision for your needs.
How to select a BLE module
There are a few key considerations to keep in mind when selecting a BLE module. These include:
- Does the module support the BLE features that your project requires?
- Is it multi-protocol capable if your project requires a multi-radio system?
- Antenna type, certification, and compliance?
- The module’s core, interfaces, operating temperature, RF performance?
- Is the module vendor reputable; In terms of both support and quality?
- OTA (over-the-air) updates support?
- Power consumption?
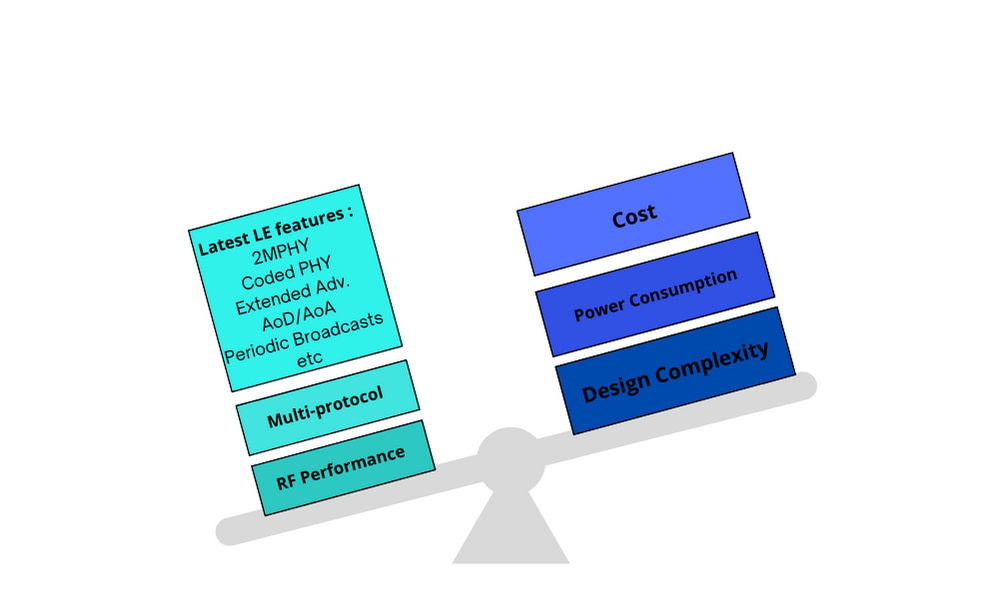
BLE support:
If your application needs a higher transmission throughput, then look for modules that support 2M PHY or advertisement packet extension. For longer ranges, then modules that support LE Coded PHY. For indoor location & positioning and tracking applications, you’ll want a module that supports Angle of Arrival (AoA) or Angle of Departure (AoD) mechanisms.
The list can go on and on, but the main criteria should be the features required by your application.
Multi-protocol capability:
Are you working on a project that requires multiple radios? If yes, you should look for modules with built-in support for multiple protocols.
For example, if your project uses both Zigbee and BLE, you’ll want to find a module that can support both protocols. This will save you the hassle of having to design and build two separate radio systems.
Usually, the module will contain only a single radio chipset, so support for both protocols will be done in a time-plexed manner. Make sure you keep that in mind since it could impose some new limitations and capabilities for each of the supported protocols.
Antenna type, certification, and compliance:
The next thing to consider is the type of antenna that is used by the module.
The antennas for Bluetooth modules are mainly classified into two types – omnidirectional antenna and directional antenna:
- An omnidirectional antenna radiates the signals to a 360-degree area to maximize the coverage rate.
- Directional antennas focus the radio signals in a particular direction.
The type of antenna you need will depend on your application requirements. For example, if your device is used in various orientations, you may have to attempt omnidirectional coverage with a module that uses an omnidirectional antenna.
And if your product is enclosed in solid metal, and its antenna needs to radiate away from the enclosure, not into it, then a directional antenna is required.
In terms of certification & compliance, many module manufacturers market their products as pre-certified or tested. This is good news for non-traditional RF manufacturers who want to integrate the wireless module into their products but lack the RF development experience.
Core, interfaces, operating temperature, and RF performance:
The core is the microprocessor, a.k.a brain, of the module, and it decides the module’s processing capabilities. Another important factor is the module’s interfaces. How the module connects to the peripherals outside itself is crucial in determining compatibility. Choose a module with enough processing power for your application.
Additionally, the module’s operating temperature should be able to work in the same temperature range as your product.
Lastly, a module with high RF sensitivity and output power gives you a better link budget and caters to more range without needing an external amplifier.
Keep your product’s needs in mind, and the onus to finding the right module will be much simpler.
Reputable BLE module vendor:
You should always pick a module vendor with a good reputation and strong technical support structure. They will help you get your product into the market quickly while providing quality modules that are up-to-date in terms of security features, SDKs, etc.
OTA updates:
OTA (over-the-air) updates are an important feature for commercial and industrial applications. If your product is going to be deployed in the field, you’ll want a module that has OTA support so you can update the firmware, fix bugs, and add new features wirelessly promptly. OTA updates reduce the need for costly downtime and technical visits.
Power consumption:
Power consumption is important when it comes to BLE products. This is because most of these products use current-constrained power sources, like lithium-ion coin cell batteries.
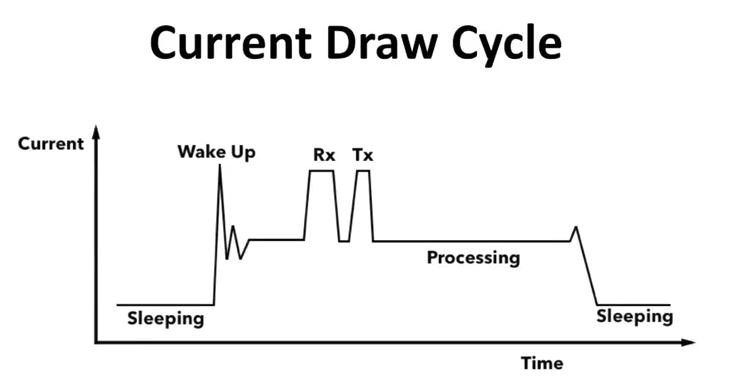
The module’s CPU and the radio will be some of the most power-hungry components in your product. When it comes to how much power a module uses while in transmit, receive, and sleep modes, you should select one with the most power-saving design to cater to the expected battery life of your product.
Other parameters:
There are many other factors you’ll want to think about, and these include the packaging dimensions, automatic sleep/activation, development tools, and price.
Common BLE Modules
Some of the popular BLE modules are listed below. This is not an exhaustive list, but it should give you a good starting point in your search for the right module for your project.
💡 Note: Click on each table to view it in fullscreen mode.
1. Nordic Semiconductor

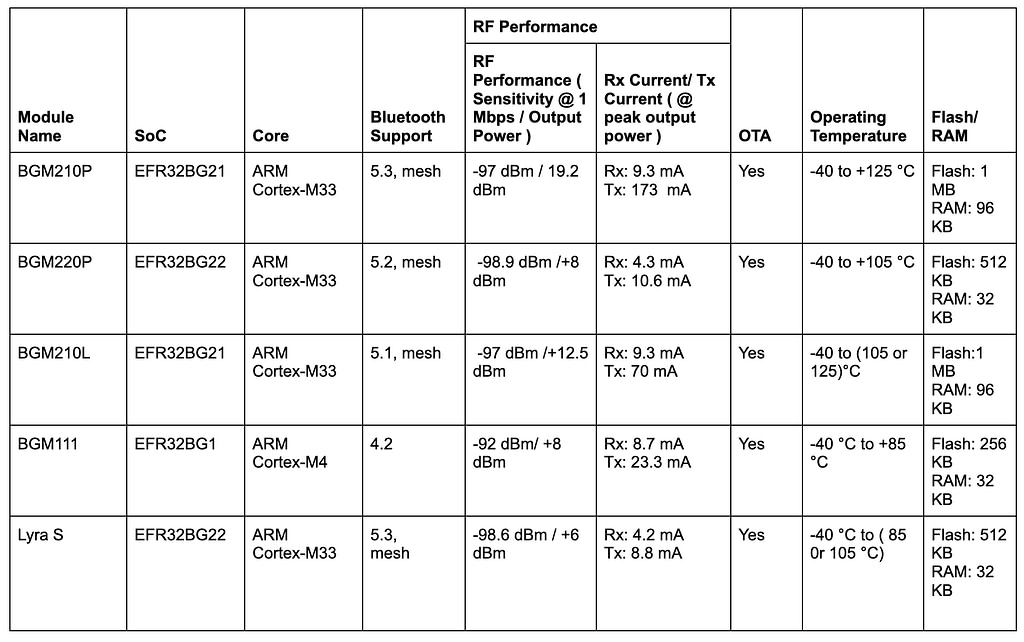
2. Silicon Labs
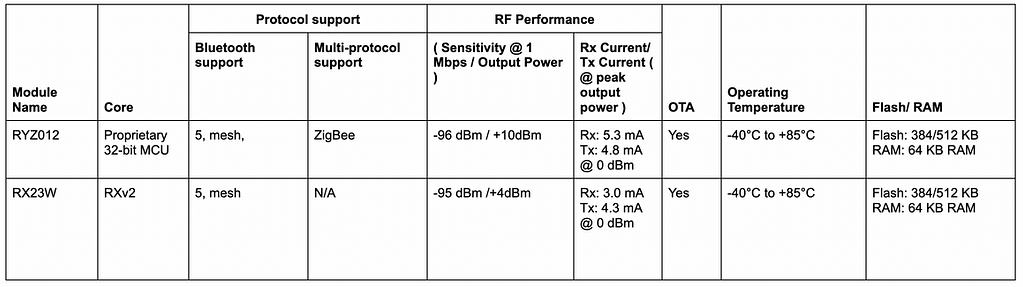
3. Renesas Semiconductor (Dialog Semiconductor)
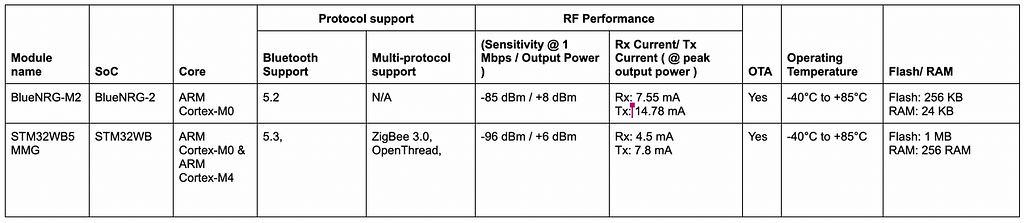
4. STMicroelectronics
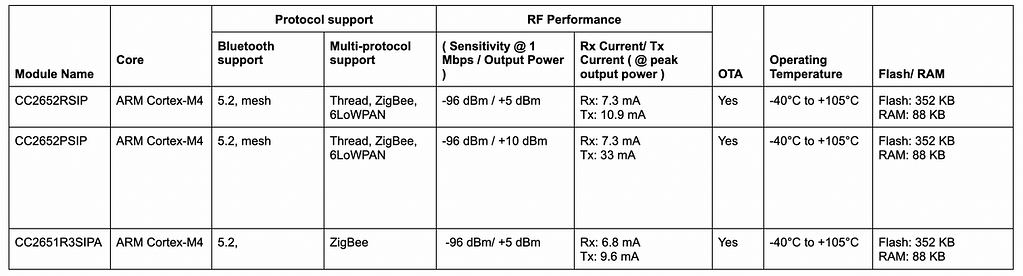
5. Texas Instruments (TI)
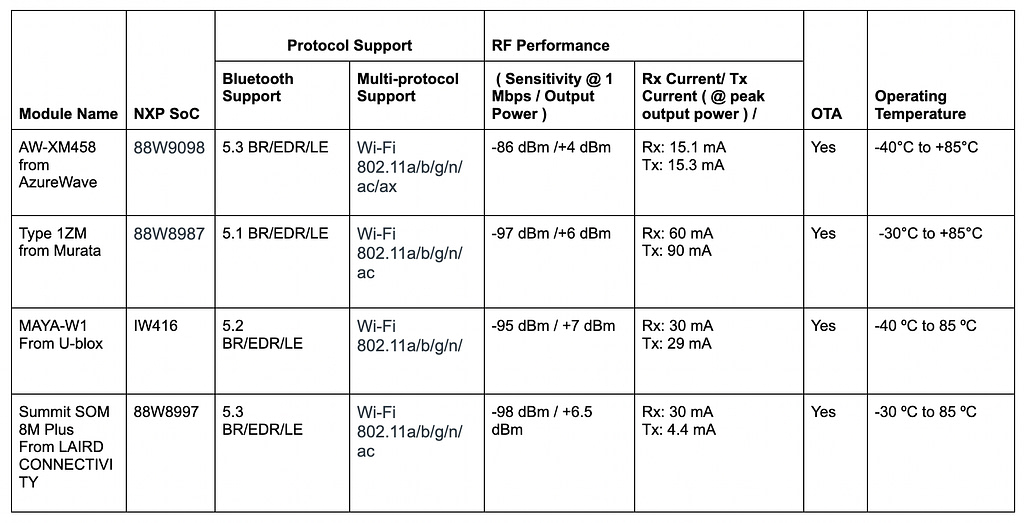
6. NXP
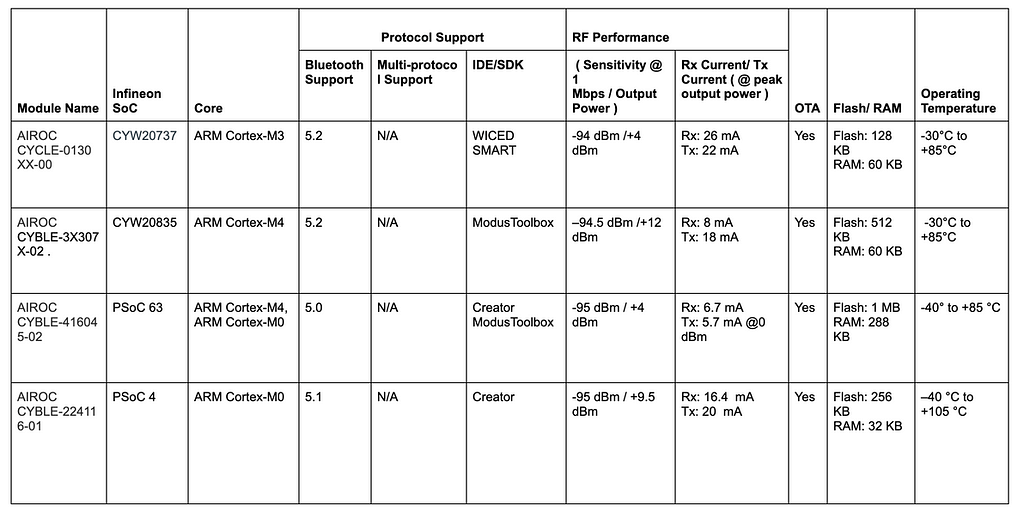
7. Infineon (Cypress)
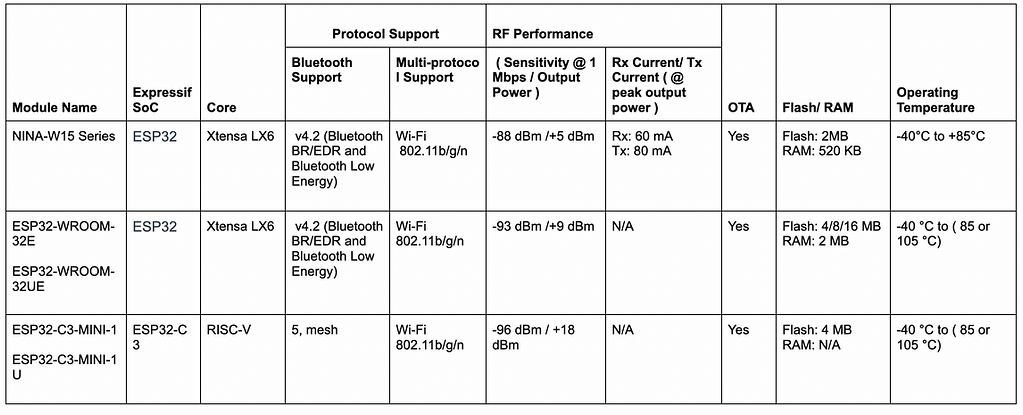
8. Espressif (ESP32)
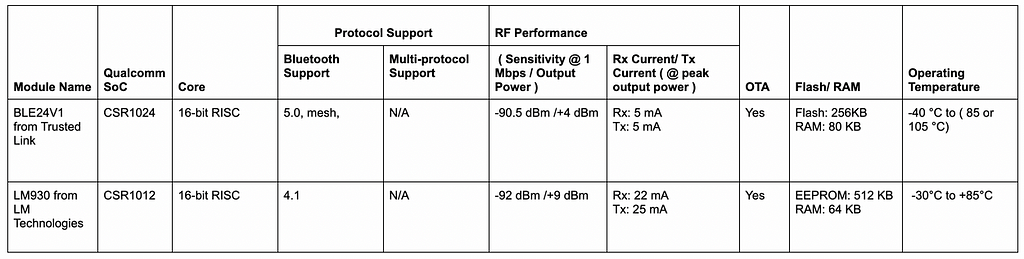
9. Qualcomm
Let’s Recap
So, what’s the best BLE module for your project? It depends mostly on your application needs and budget.
If you are looking for a more feature-rich module, the higher the price tag will be. If you need a module with a good range, then you’ll have to make sure it has high sensitivity and output power. And finally, always select a reputable vendor with good technical support.
Are you camping between a Bluetooth Module vs. a BLE SoC? Check out our Chipset vs. Module Bluetooth LE Solutions guide to help you decide.







